Highest Purity
Lowest Endotoxin
Lowest Metals
Lowest Bioburden
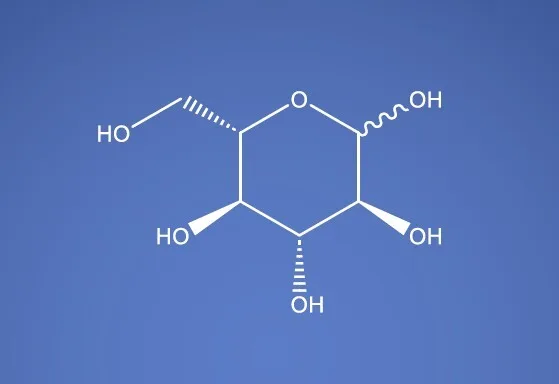
Glucose (Dextrose) USP EP BP JP ChP
Molecular Formula
C6H12O6
CAS No
Molecular Weight
Solubility in Water
Boiling Point
Melting Point
Quality Level
Parenteral Excipient Grade cGMP
Suitable for Injectable Biologic & Vaccine Formulations
Suitable for Upstream Biologic Protein Production Feeds
Glucose is a simple sugar and a key carbohydrate in biology. It is a monosaccharide with the molecular formula C₆H₁₂O₆ and is one of the primary sources of energy for living organisms. Glucose is essential for cellular respiration and is a fundamental building block for various complex carbohydrates and biomolecules.
In the context of biologic production, particularly in upstream processes involving the cultivation of cells to produce proteins, glucose serves as a primary feed component. Its role as a feed is crucial for optimizing cell growth, metabolism, and the production of high-quality biologic products.
ATP Production: Glucose is metabolized through glycolysis, where it is converted into pyruvate while generating ATP, the energy currency of the cell. This energy is essential for various cellular processes, including protein synthesis and cell maintenance.
NADH Production: In addition to ATP, glycolysis produces NADH, which is used in oxidative phosphorylation to generate further ATP, enhancing the energy supply for high-yield protein production.
Building Block for Biomolecules: Glucose provides carbon skeletons necessary for the biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, lipids, and other essential biomolecules required for cell growth and protein expression.
Precursor for Polysaccharides: It is a precursor for polysaccharides like glycogen, which cells use as energy storage molecules.
Proliferation: Glucose supports rapid cell growth and division by supplying energy and essential building blocks.
Maintenance of Cell Viability: Adequate glucose levels help maintain cell viability, which is critical for sustained protein production.
Regulation of Metabolic Pathways: The presence of glucose can influence the expression of genes involved in protein synthesis. It can modulate metabolic pathways that directly affect the yield and quality of the target protein.
Control of Post-Translational Modifications: Glucose availability can affect glycosylation patterns, which are important for the activity and stability of many biologics.
pH Regulation: The metabolism of glucose can help stabilize the pH of the culture medium, as some metabolic pathways generate acidic byproducts that need to be buffered.
Osmotic Balance: Glucose contributes to maintaining the osmotic balance in the culture medium, providing a stable environment for cells.
Fed-Batch Cultivation: Glucose is often added in a controlled manner in fed-batch processes to maintain optimal concentrations. This helps avoid depletion, which could lead to reduced cell growth and productivity.
Reduced Byproduct Formation: Controlled glucose feeding minimizes the production of inhibitory byproducts like lactate and acetate, which can accumulate if glucose is present in excess.
Consistency and Reliability: Using glucose in feed strategies helps ensure consistent product yield and quality by providing a steady nutrient supply.
Customization of Culture Conditions: Glucose levels can be adjusted to meet specific production needs, such as enhancing the expression of a target protein or minimizing unwanted metabolic shifts.
Glucose is an integral component of feed strategies in upstream biologic production. By providing essential energy, carbon, and regulatory functions, glucose supports the efficient growth and productivity of cell cultures. Proper management of glucose feeding is crucial to achieving high yields and quality of biologic products, making it a vital aspect of bioprocess optimization.
Pfanstiehl Brand High Purity – Low Endotoxin – Low Metals Glucose was developed specifically for biopharmaceutical commercial manufacturing and is produced under full ICH-Q7 cGMP conditions in the United States to the highest quality and purity standards.
Pfanstiehl Brand Glucose is compliant with USP (United States), EP (European), BP (United Kingdom, JP (Japanese) and ChP (Chinese) Pharmacopoeia.
Because of these stringent manufacturing specifications and quality systems, you can be assured that Pfanstiehl’s Glucose will be of the highest quality & consistency from batch to batch and the safest available for use in your manufacturing or research application.
Glucose (Dextrose) – Plant Derived
Highest – Compendial Parenteral Excipient Grade GMP
Highest Purity
Lowest Endotoxin
Lowest Metals
Lowest Bioburden
USP
EP
BP
JP
ChP
Upstream Protein Production & Feed Applications
Glucose (Dextrose) – Plant Derived
Highest – Compendial Parenteral Excipient Grade GMP
Highest Purity
Lowest Endotoxin
Lowest Metals
Lowest Bioburden
USP
EP
BP
JP
ChP
Upstream Protein Production & Feed Applications
100g, 1kg, 5kg, 10kg, 25kg, and 50kg